Health
Oridzin: An Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Natural Compound

Oridzin is a naturally occurring chemical present in some plants, including Scutellaria baicalensis, a Chinese herb. For millennia, oridzin has been used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a wide range of illnesses, including cancer, allergies, infections, and inflammation. Oridzin’s potential health advantages, particularly for blood sugar management, cardiovascular health, and skin health, have also drawn scientific study. This post will discuss how to use oridzin in your daily routine and some of the health advantages of the supplement that have been supported by research.
Oridzin for Healthy Skin
It has been shown that oridzin has positive internal and exterior impacts on skin health. By encouraging the skin’s natural moisturizer, hyaluronic acid, to be produced, oridinzin may help enhance the hydration, suppleness, and smoothness of the skin. Scavenging free radicals and boosting the activity of antioxidant enzymes, oridzin may help shield the skin from UV rays and oxidative stress. By preventing the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing the activation of NF-kB, a crucial regulator of inflammation, oridzin may help lessen skin inflammation and redness. Because oridzin modulates the immune system and inhibits the development of bacteria and fungus, it may also aid in the prevention or treatment of skin conditions such as dermatitis, psoriasis, acne, and eczema.
Oridzin may be used topically as a cream, gel, or serum, or taken orally as a supplement to support healthy skin. Oral consumption of 200–400 mg of origin split into two or three doses each day, is advised. Depending on the product and the state of the skin, 0.5–2% is the ideal concentration of origin for topical application. Additionally, you should search for goods that have additional organic components like niacinamide, green tea, resveratrol, and vitamin C that may strengthen the benefits of oridzin.
Oridzin for Controlling Blood Sugar
Blood sugar management has been shown to benefit from oridzin, particularly in those with prediabetes or diabetes. By boosting insulin production, preventing the breakdown of glycogen, and improving glucose absorption into the cells, origin may help reduce blood glucose levels. Oridzin activates the AMPK pathway, a crucial regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, which may help lower insulin resistance and increase insulin sensitivity. Oridzin lowers oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. This means that it may help stop or delay the development of diabetic complications like diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
You may take origin orally as a supplement to control blood sugar levels. You can take it by itself or in conjunction with other antidiabetic medications like metformin, glibenclamide, or pioglitazone. Oral consumption of 200–600 mg of origin per day, split into two or three doses, is advised. Prior to starting origin, you should also routinely check your blood glucose levels and speak with a healthcare provider, particularly if you are taking any drugs or have any medical issues.
Oridzin for Heart-Related Conditions
It has been shown that oridzin improves cardiovascular health, particularly in those with atherosclerosis, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia. By relaxing blood arteries, decreasing the activity of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and blocking the synthesis of endothelin-1, a powerful vasoconstrictor, origin may help reduce blood pressure. Additionally, origin may reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels by promoting lipoprotein clearance, reducing the production of fatty acids, and modifying the expression of genes related to lipid metabolism. Oridzin also lowers oxidative stress, inflammation, and smooth muscle cell proliferation in the arterial wall, which may help prevent or cure atherosclerosis, or the accumulation of plaque in the arteries.
You may take origin orally as a supplement to benefit your cardiovascular health. You can take it by itself or in conjunction with other cardioprotective medications like statins, aspirin, or omega-3 fatty acids. Oral consumption of 200–800 mg of origin, split into two or three doses each day is advised. Prior to using oridzin, you should also routinely check your cholesterol and blood pressure readings and speak with a healthcare provider, particularly if you are taking any drugs or have any medical concerns.
In summary
A naturally occurring substance with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities is uridzin. By modifying several molecular pathways and cellular processes, the origin may assist in enhancing cardiovascular health, blood sugar management, and skin health. Oridzin is available as a product to be applied topically or taken orally as a supplement. Although the origin is typically safe and well-tolerated, some individuals may have negative effects or interactions with other drugs. As a result, you should always get medical advice before taking oridzin and make sure you follow all dose and use guidelines.

Health
What criteria do medical recruiters examine when hiring a physician for a hospital position?

In the fast-paced realm of healthcare, the pivotal role of a physician extends beyond clinical expertise—it encompasses a delicate blend of skills and attributes that resonate with the specific needs of a hospital. Picture this: a dedicated doctor recruiter meticulously sifting through a pool of candidates, seeking the ideal physician to join the hospital’s dynamic team.
What criteria do medical recruiters examine when hiring a physician for a hospital position? As we delve into this critical aspect of healthcare staffing, we’ll unravel the key elements that elevate a physician from a mere applicant to an indispensable asset for a hospital, shedding light on the nuanced considerations that drive the decisions of these discerning doctor recruiters.
Join us on a journey through the intricacies of physician recruitment, where qualifications meet the art of matching the right medical professional with the unique demands of a hospital environment.
Introduction
The demand for highly qualified physicians in hospital settings is ever-increasing. The right hire can significantly impact patient care, staff morale, and the overall success of a medical institution. Understanding the criteria that medical recruiters focus on is crucial for both aspiring physicians and those responsible for the hiring process.
Educational Background
Medical Degree and Specialization
The foundation of a physician’s career lies in their educational background. Recruiters scrutinize the medical degree and specialization, ensuring it aligns with the needs of the hospital. Specialized skills are often required for specific departments, making this a critical consideration.
Residency and Fellowship Training
Beyond the degree, recruiters delve into residency and fellowship training. The hands-on experience gained during these periods shapes a physician’s clinical skills and expertise. Hospitals seek candidates whose training aligns with the services they offer.
Clinical Experience
Years of Practice
The number of years a physician has been in practice is a key factor. While experienced candidates bring a wealth of knowledge, recruiters also consider the freshness of recent graduates who might bring innovative approaches.
Expertise in Specialized Areas
Recruiters assess a physician’s expertise in specialized areas. Whether it’s cardiology, neurology, or surgery, the hospital’s needs dictate the specific skills they seek in a candidate.
Licensure and Certification
State Licensing
State licensing is a non-negotiable aspect of a physician’s eligibility. Recruiters ensure that candidates are licensed to practice in the state where the hospital is located.
Board Certification
Board certification adds an extra layer of assurance regarding a physician’s proficiency. Hospitals often prioritize candidates who have achieved board certification in their respective specialties.
Soft Skills and Interpersonal Qualities
Communication Skills
Effective communication is paramount in healthcare. Recruiters evaluate a physician’s ability to communicate clearly with patients, colleagues, and support staff.
Team Collaboration
Hospital environments thrive on collaboration. Physicians who can seamlessly work in a team contribute to a positive workplace culture, enhancing patient care outcomes.
Empathy and Patient Care
Empathy is the cornerstone of patient care. Recruiters assess a physician’s ability to connect with patients on a personal level, fostering trust and comfort.
Adaptability and Flexibility
Handling Stressful Situations
Medical settings can be intense, requiring physicians to handle stress with composure. Recruiters gauge a candidate’s ability to navigate high-pressure situations effectively.
Willingness to Learn and Adapt
The medical field is evolving rapidly. Recruiters seek candidates who demonstrate a proactive approach to ongoing learning and adaptation to new medical technologies and practices.
Cultural Fit
Alignment with Hospital Values
Hospitals often have distinct values that guide their approach to patient care. Recruiters look for candidates whose values align with those of the institution.
Understanding Diversity
In a diverse healthcare landscape, understanding and respecting various cultures and backgrounds is crucial. Recruiters assess a physician’s cultural competence to ensure comprehensive and inclusive patient care.
Leadership and Management Skills
Ability to Lead Teams
Physicians, especially in leadership roles, must exhibit strong leadership skills. Recruiters evaluate a candidate’s ability to lead teams effectively and contribute to the hospital’s overall strategic goals.
Decision-Making Skills
Quick and informed decision-making is essential in healthcare. Recruiters seek candidates who showcase sound judgment and critical decision-making skills.
Technological Proficiency
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Knowledge
The integration of technology in healthcare is inevitable. Recruiters look for physicians who are proficient in using electronic health records, ensuring efficient and accurate patient information management.
Embracing Technological Advances
Hospitals value candidates who embrace technological advances in the medical field. A tech-savvy physician can contribute to the seamless adoption of innovative practices within the institution.
Research and Publications
Contribution to Medical Knowledge
Physicians involved in research contribute significantly to advancing medical knowledge. Recruiters consider a candidate’s research contributions, which can enhance the hospital’s reputation and academic standing.
Published Research and Journals
Published research and articles in reputable journals showcase a physician’s commitment to staying at the forefront of medical advancements. Recruiters value candidates who actively contribute to the academic community.
Networking and Professional Relationships
Collaborations with Other Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare is a collaborative effort. Recruiters look for candidates who have a history of successful collaborations with other healthcare professionals, fostering a supportive and cooperative work environment.
Participation in Medical Associations
Active participation in medical associations indicates a commitment to ongoing professional development. Recruiters appreciate physicians who engage with the larger medical community.
References and Recommendations
Importance of References
References provide insights into a candidate’s professional conduct. Recruiters carefully consider references to ensure a candidate’s compatibility with the hospital’s work culture.
Impact of Professional Recommendations
Recommendations from colleagues and mentors carry weight. Positive recommendations can reinforce a candidate’s suitability for a hospital position.
Legal and Ethical Compliance
Adherence to Medical Ethics
Medical ethics are non-negotiable. Recruiters assess a candidate’s commitment to ethical medical practices, ensuring patient safety and trust.
Understanding Legal Obligations
A sound understanding of legal obligations in healthcare is essential. Recruiters seek candidates who are knowledgeable about and compliant with legal requirements in their practice.
Interview Performance
Key Questions and Scenarios
The interview is a crucial step in the hiring process. Recruiters design questions and scenarios to assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills, ethical decision-making, and overall suitability for the role.
Assessment of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a prized skill in healthcare. Recruiters gauge a candidate’s ability to think critically and make informed decisions in real-time situations.
Conclusion
In the highly competitive landscape where a doctor recruiter play a pivotal role, the criteria for hiring physicians transcend mere clinical competence. Recruiters meticulously assess educational backgrounds, clinical experience, soft skills, adaptability, cultural fit, leadership qualities, technological proficiency, research contributions, professional relationships, references, legal compliance, and interview performance.
Striking the right balance among these criteria is essential to ensure hospitals welcome physicians who not only meet medical requirements but also contribute to fostering a positive and collaborative healthcare environment.
Health
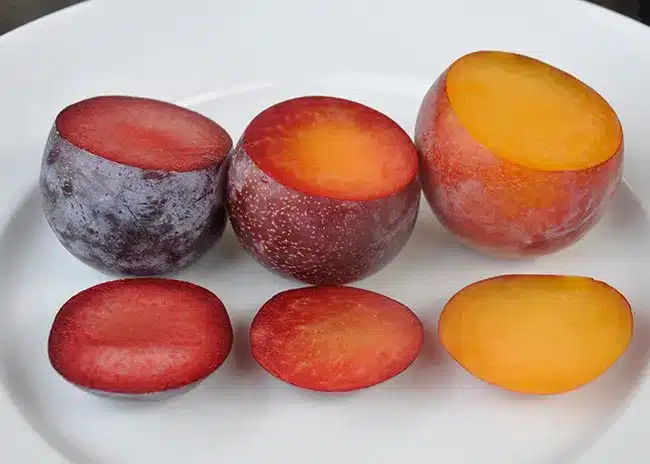
Exploring the Unique Charm of Plumcots: A Perfect Blend of Plums and Apricots
Health
Sensual Massage: An Intimate Exploration of Connection and Pleasure

-
General10 months ago
Orchard Grass (Dactylis glomerata): A Botanical Epic
-
Lifestyle10 months ago
Fascinating World of ‘Cristoferideas’ and their Viral TikTok Video
-
Technology10 months ago
GPT66x: Boosting Talks with Transformer & Optimization
-
Gaming1 year ago
Scholardle: The Academic Word Guessing Game
-
Lifestyle10 months ago
Meet Katie Sakov San Francisco’s Talented Writer and Editor
-
Lifestyle10 months ago
Shine Bright with Mazalti: Jewelry Collections
-
Technology1 year ago
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT PISIPHON VPN
-
Blog1 year ago
Record Of The Mightiest Lord Chapter 1